Why now is the time to embrace automated spectrum monitoring
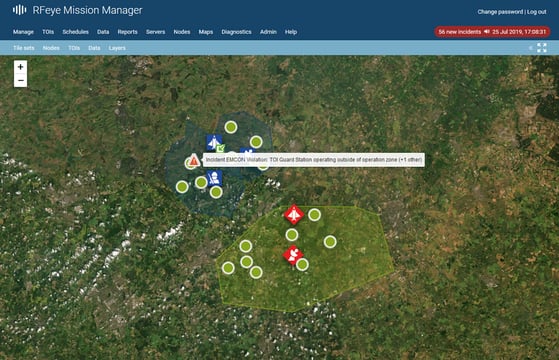
In a world where digital communication is vital to the success of commercial, civilian, emergency, and military operations, reliable and secure radio frequency (RF) spectrum monitoring has become more crucial than ever. It’s especially challenging in crowded cities, border regions, bases, and public safety applications, where the radio spectrum is prone to interference or disturbance from neighboring communications.
To address these challenges, organizations must have the tools to manage an ever-evolving and complex RF landscape, often with limited resources. This is why more spectrum managers are turning toward automated spectrum monitoring systems that provide real-time operational oversight, detailed spectrum usage management, customizable alerts, and wide-area coverage to meet their unique use case.
How is automated spectrum monitoring different? And how can organizations across industries use it for their increasingly complex missions?
Automated spectrum monitoring systems are no longer just nice to have
Industry-leading spectrum monitoring systems are vital, providing a mission-critical function. Here are three reasons why they’re no longer just nice to have:
1. Automation replaces highly manual, complex, and time-intensive monitoring tasks.
By automating previously manual, complex, and time-consuming tasks, spectrum managers can now efficiently collect and process actionable intelligence from a network of RF signal receivers, no matter how geographically diverse.
With automation, organizations can overcome the traditional limitations that come with manual monitoring. This can range from fatigue and training gaps to human error and the monotony of having to constantly watch for anomalies in a crowded spectrum.
Automation gives spectrum monitors the ability to identify and analyze anomalies with greater precision and accuracy. Rather than facing a wall of constantly flowing data, automation simplifies the information into an actionable view or dashboard that can be tailored, filtered, and sorted for each unique use case.
These customizable dashboards can also be supplemented with automated triggers or push notifications that can be set up to help teams cut through the noise and act on preconfigured alerts based on defined severity criteria. This ensures that organizations can quickly respond to any potential threats or disruptions in the RF spectrum.
2. Automation delivers real-time, geographically accurate, and actionable views of RF activity.
Automation also delivers spectrum managers a real-time, geographically accurate, and actionable view of RF activity. With the help of detailed map overlays, users can easily visualize and understand the current RF activities in their operating areas and use interactive and intuitive interfaces to tailor spectrum monitoring to their specific use case.
Unlike traditional monitoring systems, automated systems can geolocate signals of interest based on frequency, bandwidth, signal location, time, and power. This allows organizations to immediately pinpoint sources of interference while continuing to record and monitor other signals. This capability is especially crucial in crowded cities, border regions, and public safety complex areas, where the spectrum is prone to interference or disturbance from multiple locations and sources.
Armed with this actionable view of RF activity and a network of remote, autonomous sensors, organizations can take swift and informed actions to mitigate any adverse effects on their networks or within their area of responsibility. This helps to ensure reliable and secure digital communication around the clock.
3. Automation enables scalable, flexible, and centralized signal collection and analysis.
Automation not only improves the efficiency and accuracy of signal collection and analysis but also delivers the ability to scale, adapt and centralize signal collection and analysis.
Whether for regulatory compliance, security, or spectrum management, automation allows for the deployment of a vast network of remote RF sensors and receivers. This network can collect and transmit data in real-time, providing a comprehensive view of the spectrum environment. This scalability enables organizations to manage an increasing number of RF devices and networks, optimize spectrum use, and reduce the impact of interference on their and neighboring communication.
Finally, centralizing the collection and analysis of signals enables a more streamlined and efficient approach to spectrum management, enabling organizations to respond to issues more quickly and effectively and match their operational needs with their existing resources.
Use cases for automated spectrum monitoring
Automated spectrum monitoring can be useful in a variety of fields and industries, especially for:
- Wireless network management: Automated spectrum monitoring can help network operators manage wireless networks more efficiently by identifying and locating sources of interference, optimizing the use of available spectrum, and improving network performance.
- Public safety: Public safety agencies can use automated spectrum monitoring to ensure emergency services can communicate effectively without interference from other wireless devices or networks.
- Military and defense: Military and defense organizations can use automated spectrum monitoring to detect and locate sources of interference, identify and geolocate potential threats, manage operational spectrum usage, and ensure secure and reliable communication.
- Broadcasting: Automated spectrum monitoring can help broadcasting authorities ensure broadcasters are operating within their allocated frequencies and not causing interference for other services or networks.
- Satellite communications: Automated spectrum monitoring can prevent interference with established satellite communications and other wireless networks, ensuring reliable and secure communication.
- Aviation: Automated spectrum monitoring can help aviation authorities prevent interference between aircraft communication and navigation systems and other wireless devices or networks, ensuring safe and reliable air travel.
In each of these use cases, automated monitoring can work in conjunction with the ability to conduct historical analysis and geolocation, help with dissecting interruptions and anomalies and identify the source for follow-up action.
Revolutionize your spectrum monitoring with the power of automation
No matter the application or the scale, implementing automated spectrum monitoring is transforming not only how spectrum managers manage wireless communication but also the level of granularity and real-time analysis.
Supported by leading automated spectrum monitoring tools and autonomous RF sensors, spectrum managers, regulators, and military organizations can quickly and efficiently set up monitoring systems. These can help to detect and prevent interference, ensure secure communication, and optimize the use of the available spectrum.
As more civilian, public safety, and military operations increasingly rely on wireless communications around the clock, automated spectrum monitoring will play an essential role in ensuring smooth and reliable communication.
Jon Bradley
With over 6 years of experience, Dr Bradley enjoys close collaboration with a range of CRFS clients to help them understand how to lever CRFS technology and what advantages the RFeye ecosystem can bring in real-world scenarios. Leading our Rest of World commercial team, he brings over 30 years of experience and know-how in both theory and in practice. When not living, sleeping, and dreaming about science, he enjoys hiking with Hugo the RF retriever who often appears in his posts.
